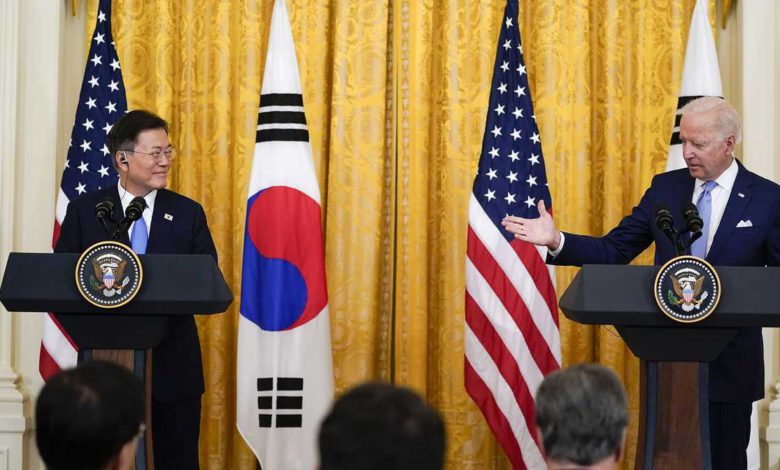
President Joe Biden on Friday said he and South Korean President Moon Jae-in remain "deeply concerned" about the situation with North Korea, and announced he will deploy a new special envoy to the region to help refocus efforts on pressing Pyongyang to abandon its nuclear weapons program.Moon, meanwhile, welcomed "America's return" to the world stage and said both leaders pledged to work closely toward denuclearization of the Korean peninsula.Biden said he was dispatching career diplomat Sung Kim, who previously served as ambassador to South Korea, to serve as the special envoy to the region.Moon said the move by Biden "reflects the firm commitment of the U.S. for exploring diplomacy and its readiness for dialogue with North Korea."Moon came to Washington seeking renewed diplomatic urgency by the U.S. on curbing North Korea's nuclear program, even as the White House signaled that it is taking a longer view on the issue. High on Biden's list for the meeting as well: coordination in vaccine distribution, climate change and regional security concerns spurred by China.Their meeting was only Biden's second in-person session with a foreign leader because of the coronavirus pandemic.Moon said after the meeting the two had "a very frank dialogue like old friends" and emphasized the need for cooperation on security issues in the region."The most urgent common task that our two countries must undertake is achieving complete denuclearization and permanent peace on the Korean peninsula," he said.Moon said the two "reaffirmed the strength" of the nations' alliance and "affirmed the common vision for developing it into an even stronger one."Their formal talks in the afternoon ran long, Biden said in earlier remarks, noting his staff interrupted repeatedly to warn they were over time. "But I enjoyed the meeting so much that it caused us to move everything back," Biden said, as he highlighted the two countries' "long history of shared sacrifice."Moon said "The world is welcoming America's return," an oblique reference to former President Donald Trump's attempts to disengage on some aspects of American diplomacy.The White House announced last month that it had completed a review of North Korea policy and Biden would veer from the strategies of his two most recent predecessors, rejecting both Trump's deeply personal effort to win over North Korean leader Kim Jong Un and Barack Obama's more hands-off approach. But the administration has yet to detail what its third-way effort to try to prod the North to abandon its nuclear program will look like.Moon started his day at the White House complex by meeting with Vice President Kamala Harris and top Biden advisers. Moon also participated in a Medal of Honor ceremony for Ralph Puckett, a 94-year-old Army veteran who was celebrated for his gallantry during the Korean War more than 70 years ago."Without the sacrifice of veterans including Colonel Puckett ... freedom and democracy we enjoy today couldn't have blossomed in Korea," said Moon, who hailed Puckett as "true hero."Moon, who will leave office next May, is eager to resume stalled talks between Washington and Pyongyang and between Seoul and Pyongyang. But the Biden administration, which confirmed in March that it had made outreach efforts to the North without success, has been less enthusiastic about the idea of direct negotiations in the near term. Asked Thursday whether Biden was open to holding direct talks with Kim, as Trump did twice, press secretary Jen Psaki demurred."I don't expect that to be top on his agenda," she said of Biden.Still, Moon made clear before the meeting that he would nudge Biden to renew diplomatic efforts with the North."I will not be pressed by time or become impatient during the remainder of my term," Moon told reporters this month. "However, if there is an opportunity to restart the clock of peace and advance the peace process on the Korean Peninsula, I will do everything I can."A senior administration official, who was not authorized to discuss the matter publicly and briefed reporters on Moon's visit on the condition of anonymity, sidestepped questions about whether the administration was willing to offer North Korea sanctions relief to begin dismantling its nuclear and ballistic weapons programs.The official said the U.S. was hoping to chart a "flexible" way forward, well aware of where past efforts went awry.Biden was also expected to use the meeting to press South Korea to adopt a more ambitious 2030 target for curbing carbon emissions and to urge Seoul to do more to counter China's growing influence in the Indo-Pacific region. Moon was expected to seek Biden's assistance with helping South Korea boost its coronavirus vaccine supply. South Korea has vaccinated only about 5% of its population.Biden also wanted Moon to take a strong stance on China's activity toward Taiwan and other provocative moves Beijing has made in the region. Biden has sought to rally Pacific allies to coordinate on China, which Biden sees as the United States' fiercest economic competitor. Biden, in the early going of his presidency, has spoken out about concerns with Beijing's trade policies and human rights record and has also highlighted regional allies' concerns about an increasingly assertive Chinese military.Biden has taken note of Japan's concerns that China's growing military activity and broad territorial claims present a security threat. Japan is locked in a dispute with China over Beijing's claim to the Japanese-controlled Senkaku Islands, called Diaoyu in China, in the East China Sea. He's also looked to strengthen relations with India, which has been tested by a military standoff with China along their disputed border in eastern Ladakh.But South Korea could be more reluctant to speak out about China, an important trading partner that it also sees as key in dealing with the Kim regime. Moon told reporters at the leaders' joint press conference after their meeting that "there was not pressure" on the issue applied by Biden.Michael Green, who served as senior director for Asia on the National Security Council during the George W. Bush administration, said South Korea's situation is difficult. "This South Korean policy of strategic ambiguity is proving increasingly awkward and almost untenable for Seoul because other middle powers that are not the U.S. or Japan ... are adjusting their China policies," said Green, who is senior vice president for Asia and Japan Chair at the Center for Strategic and International Studies.Moon on Thursday visited Arlington National Cemetery just outside Washington and laid a wreath at a memorial to Americans killed during the Korean War. He also visited the U.S. Capitol to meet with Democratic House Speaker Nancy Pelosi.
President Joe Biden on Friday said he and South Korean President Moon Jae-in remain "deeply concerned" about the situation with North Korea, and announced he will deploy a new special envoy to the region to help refocus efforts on pressing Pyongyang to abandon its nuclear weapons program.
Moon, meanwhile, welcomed "America's return" to the world stage and said both leaders pledged to work closely toward denuclearization of the Korean peninsula.
Biden said he was dispatching career diplomat Sung Kim, who previously served as ambassador to South Korea, to serve as the special envoy to the region.
Moon said the move by Biden "reflects the firm commitment of the U.S. for exploring diplomacy and its readiness for dialogue with North Korea."
Moon came to Washington seeking renewed diplomatic urgency by the U.S. on curbing North Korea's nuclear program, even as the White House signaled that it is taking a longer view on the issue. High on Biden's list for the meeting as well: coordination in vaccine distribution, climate change and regional security concerns spurred by China.
Their meeting was only Biden's second in-person session with a foreign leader because of the coronavirus pandemic.
Moon said after the meeting the two had "a very frank dialogue like old friends" and emphasized the need for cooperation on security issues in the region.
"The most urgent common task that our two countries must undertake is achieving complete denuclearization and permanent peace on the Korean peninsula," he said.
Moon said the two "reaffirmed the strength" of the nations' alliance and "affirmed the common vision for developing it into an even stronger one."
Their formal talks in the afternoon ran long, Biden said in earlier remarks, noting his staff interrupted repeatedly to warn they were over time. "But I enjoyed the meeting so much that it caused us to move everything back," Biden said, as he highlighted the two countries' "long history of shared sacrifice."
Moon said "The world is welcoming America's return," an oblique reference to former President Donald Trump's attempts to disengage on some aspects of American diplomacy.
The White House announced last month that it had completed a review of North Korea policy and Biden would veer from the strategies of his two most recent predecessors, rejecting both Trump's deeply personal effort to win over North Korean leader Kim Jong Un and Barack Obama's more hands-off approach.
But the administration has yet to detail what its third-way effort to try to prod the North to abandon its nuclear program will look like.
Moon started his day at the White House complex by meeting with Vice President Kamala Harris and top Biden advisers. Moon also participated in a Medal of Honor ceremony for Ralph Puckett, a 94-year-old Army veteran who was celebrated for his gallantry during the Korean War more than 70 years ago.
"Without the sacrifice of veterans including Colonel Puckett ... freedom and democracy we enjoy today couldn't have blossomed in Korea," said Moon, who hailed Puckett as "true hero."
Moon, who will leave office next May, is eager to resume stalled talks between Washington and Pyongyang and between Seoul and Pyongyang. But the Biden administration, which confirmed in March that it had made outreach efforts to the North without success, has been less enthusiastic about the idea of direct negotiations in the near term.
Asked Thursday whether Biden was open to holding direct talks with Kim, as Trump did twice, press secretary Jen Psaki demurred.
"I don't expect that to be top on his agenda," she said of Biden.
Still, Moon made clear before the meeting that he would nudge Biden to renew diplomatic efforts with the North.
"I will not be pressed by time or become impatient during the remainder of my term," Moon told reporters this month. "However, if there is an opportunity to restart the clock of peace and advance the peace process on the Korean Peninsula, I will do everything I can."
A senior administration official, who was not authorized to discuss the matter publicly and briefed reporters on Moon's visit on the condition of anonymity, sidestepped questions about whether the administration was willing to offer North Korea sanctions relief to begin dismantling its nuclear and ballistic weapons programs.
The official said the U.S. was hoping to chart a "flexible" way forward, well aware of where past efforts went awry.
Biden was also expected to use the meeting to press South Korea to adopt a more ambitious 2030 target for curbing carbon emissions and to urge Seoul to do more to counter China's growing influence in the Indo-Pacific region.
Moon was expected to seek Biden's assistance with helping South Korea boost its coronavirus vaccine supply. South Korea has vaccinated only about 5% of its population.
Biden also wanted Moon to take a strong stance on China's activity toward Taiwan and other provocative moves Beijing has made in the region. Biden has sought to rally Pacific allies to coordinate on China, which Biden sees as the United States' fiercest economic competitor.
Biden, in the early going of his presidency, has spoken out about concerns with Beijing's trade policies and human rights record and has also highlighted regional allies' concerns about an increasingly assertive Chinese military.
Biden has taken note of Japan's concerns that China's growing military activity and broad territorial claims present a security threat. Japan is locked in a dispute with China over Beijing's claim to the Japanese-controlled Senkaku Islands, called Diaoyu in China, in the East China Sea. He's also looked to strengthen relations with India, which has been tested by a military standoff with China along their disputed border in eastern Ladakh.
But South Korea could be more reluctant to speak out about China, an important trading partner that it also sees as key in dealing with the Kim regime. Moon told reporters at the leaders' joint press conference after their meeting that "there was not pressure" on the issue applied by Biden.
Michael Green, who served as senior director for Asia on the National Security Council during the George W. Bush administration, said South Korea's situation is difficult.
"This South Korean policy of strategic ambiguity is proving increasingly awkward and almost untenable for Seoul because other middle powers that are not the U.S. or Japan ... are adjusting their China policies," said Green, who is senior vice president for Asia and Japan Chair at the Center for Strategic and International Studies.
Moon on Thursday visited Arlington National Cemetery just outside Washington and laid a wreath at a memorial to Americans killed during the Korean War. He also visited the U.S. Capitol to meet with Democratic House Speaker Nancy Pelosi.
Source link